
4.5 (623) · $ 2204.00 · In stock
Description
Jul 13, 2022 - PRODUCT DETAILS Includes Shipping bags, dustbag sleeper, care manual, booklet, tag.

Style 1 / 22 x 16 x 6cm / 8.8 x 6.4 x 2.4 inches – Supernfb
Soil Systems, Free Full-Text

BG - Quantifying biological carbon pump pathways with a data

KM Exact Seat Covers Tractor, Gator & Lawn Mower Seat Cover

YVES SAINT LAURENT Vinyle Round Chevron Leather Camera Crossbody Bag B

Foliar optical traits capture physiological and phenological leaf
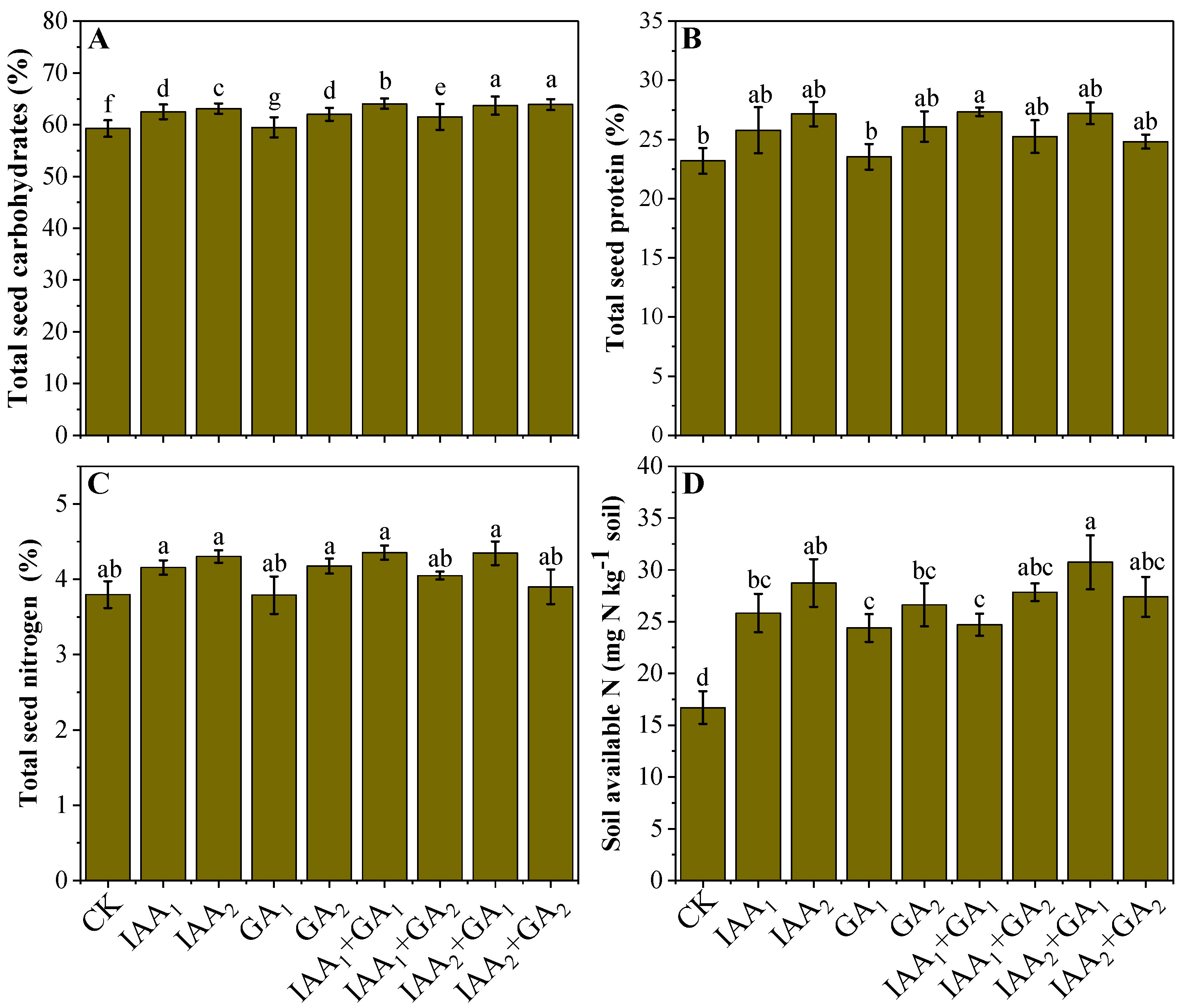
Increasing the performance of Passion fruit (Passiflora edulis
Common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) is sensitive to different types of abiotic stresses (drought, high temperature, low soil fertility, and acid soil), and this may limit its adaptation and consequently to its yield under stress. Because of this, a sister species, tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolius A. Gray), has recently gained attention in breeding for improved abiotic stress tolerance in common bean. In this study, we evaluated the adaptation of 302 accessions of tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolius A. Gray) and its wild relatives (grouped in four types of tepary bean genetic resource: cultivated, acutifolius regressive, acutifolius wild, tenuifolius wild) when grown under high temperature and acid soil conditions with aluminum toxicity in the region of Colombia. Our objective was to determine differences among four types of tepary bean genetic resource in their morpho-phenological, agronomic, and physiological responses to combined high temperature and acid soil stress conditions. We found that cultivated P. acutifolius var acutifolius presented a greater number of pods per plant, as well as larger seeds and a greater number of seeds per pod. Some traits, such as root biomass, days to flowering and physiological maturity, specific leaf area, and stomatal density, showed significant differences between types of tepary bean genetic resource, probably contributing to difference in adaptation to combined stress conditions of high temperature and acid soil conditions. The photochemical quenching (qP) was higher in cultivated P. acutifolius var. acutifolius, while energy dissipation by non-photochemical quenching (NPQ) in the form of heat and the coefficient of non-photochemical dissipation (qN) were higher in acutifolius regressive and tenuifolius wild accessions. We have identified 6 accessions of cultivated and 19 accessions of tenuifolius wild that exhibited grain yields above 1800 kg ha−1. These accessions could be suitable to use as parents to improve dry seed production of tepary bean under combined stress conditions of high temperature and acid soil.
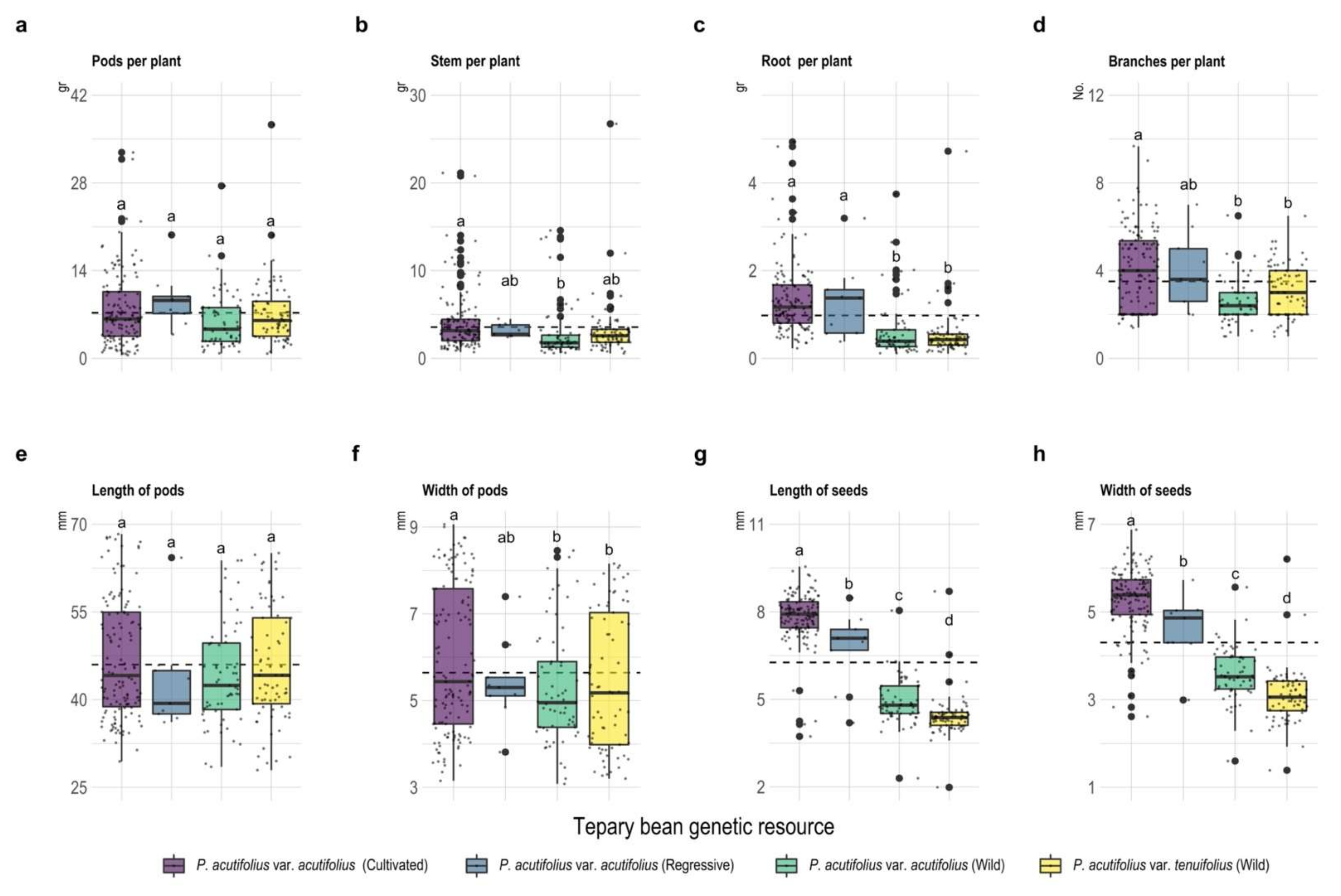
Plants, Free Full-Text

villa alegre - Pavilion Construction
Current understanding of the effects of extreme temperature on alpine evergreens is very limited for ecosystems under Mediterranean climate (characterised by a drought period in summer), despite being exceptionally biodiverse systems and highly vulnerable under a global change scenario. We thus assessed (i) seasonal change and (ii) effect of ontogeny (young vs. mature leaves) on thermal sensitivity of Erysimum scoparium, a keystone evergreen of Teide mountain (Canary Islands). Mature leaves were comparatively much more vulnerable to moderately high leaf-temperature (≥+40 and <+50 °C) than other alpine species. Lowest LT50 occurred in autumn (−9.0 ± 1.6 °C as estimated with Rfd, and −12.9 ± 1.5 °C with Fv/Fm). Remarkably, young leaves showed stronger freezing tolerance than mature leaves in spring (LT50 −10.3 ± 2.1 °C vs. −5.6 ± 0.9 °C in mature leaves, as estimated with Rfd). Our data support the use of Rfd as a sensitive parameter to diagnose temperature-related damage in the leaves of mountain plants. On a global change scenario, E. scoparium appears as a well-prepared species for late-frost events, however rather vulnerable to moderately high temperatures.
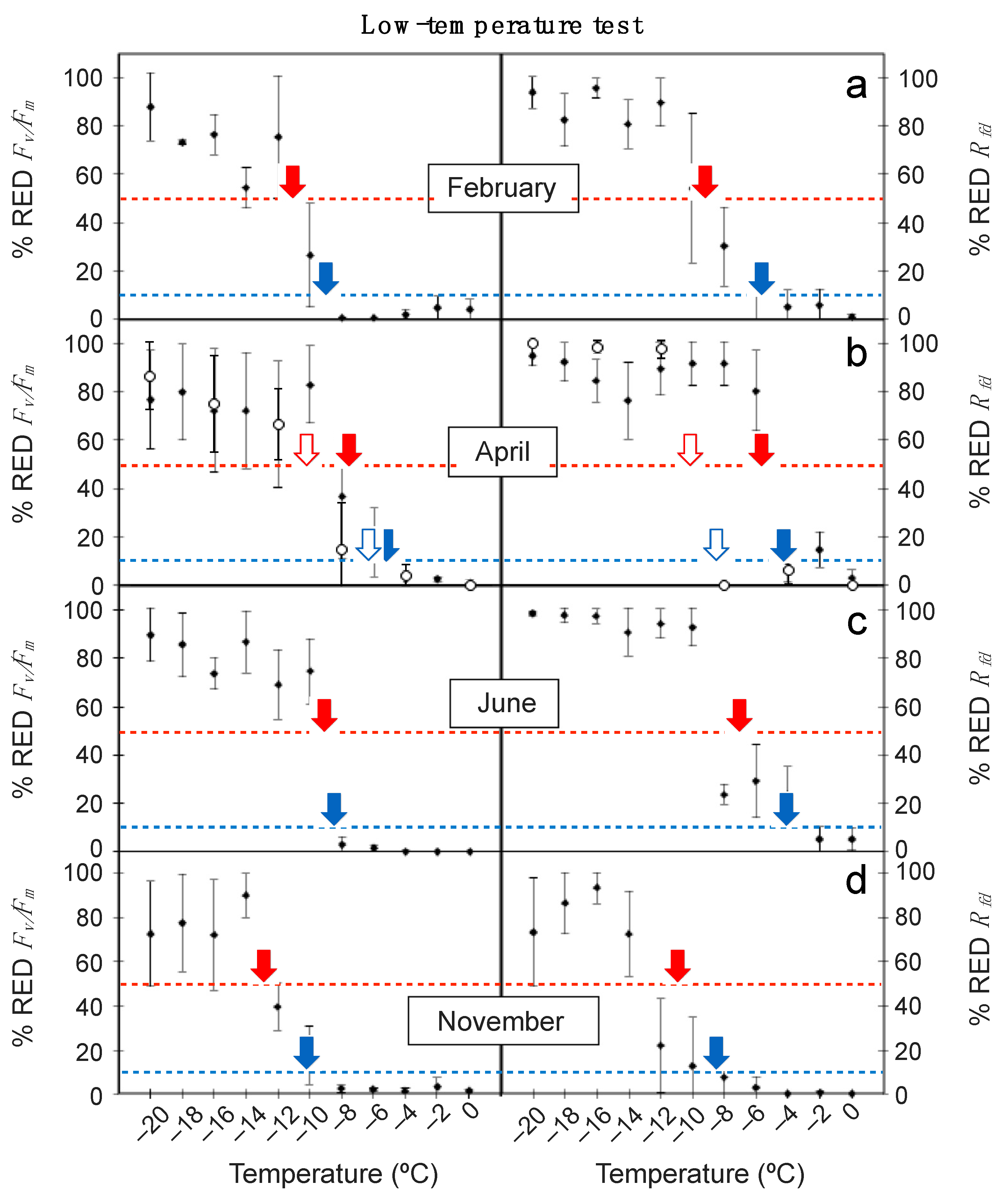
Plants, Free Full-Text
Lipid and/or polymer-based drug conjugates can potentially minimize side effects by increasing drug accumulation at target sites and thus augment patient compliance. Formulation factors can present a potent influence on the characteristics of the obtained systems. The selection of an appropriate solvent with satisfactory rheological properties, miscibility, and biocompatibility is essential to optimize drug release. This work presents a computational study of the effect of the basic formulation factors on the characteristics of the obtained in situ-forming particulates (IFPs) encapsulating a model drug using a 21.31 full factorial experimental design. The emulsion method was employed for the preparation of lipid and/or polymer-based IFPs. The IFP release profiles and parameters were computed. Additionally, a desirability study was carried out to choose the optimum formulation for further morphological examination, rheological study, and PBPK physiological modeling. Results revealed that the type of particulate forming agent (lipid/polymer) and the incorporation of structure additives like Brij 52 and Eudragit RL can effectively augment the release profile as well as the burst of the drug. The optimized formulation exhibited a pseudoplastic rheological behavior and yielded uniformly spherical-shaped dense particulates with a PS of 573.92 ± 23.5 nm upon injection. Physiological modeling simulation revealed the pioneer pharmacokinetic properties of the optimized formulation compared to the observed data. These results assure the importance of controlling the formulation factors during drug development, the potentiality of the optimized IFPs for the intramuscular delivery of piroxicam, and the reliability of PBPK physiological modeling in predicting the biological performance of new formulations with effective cost management.
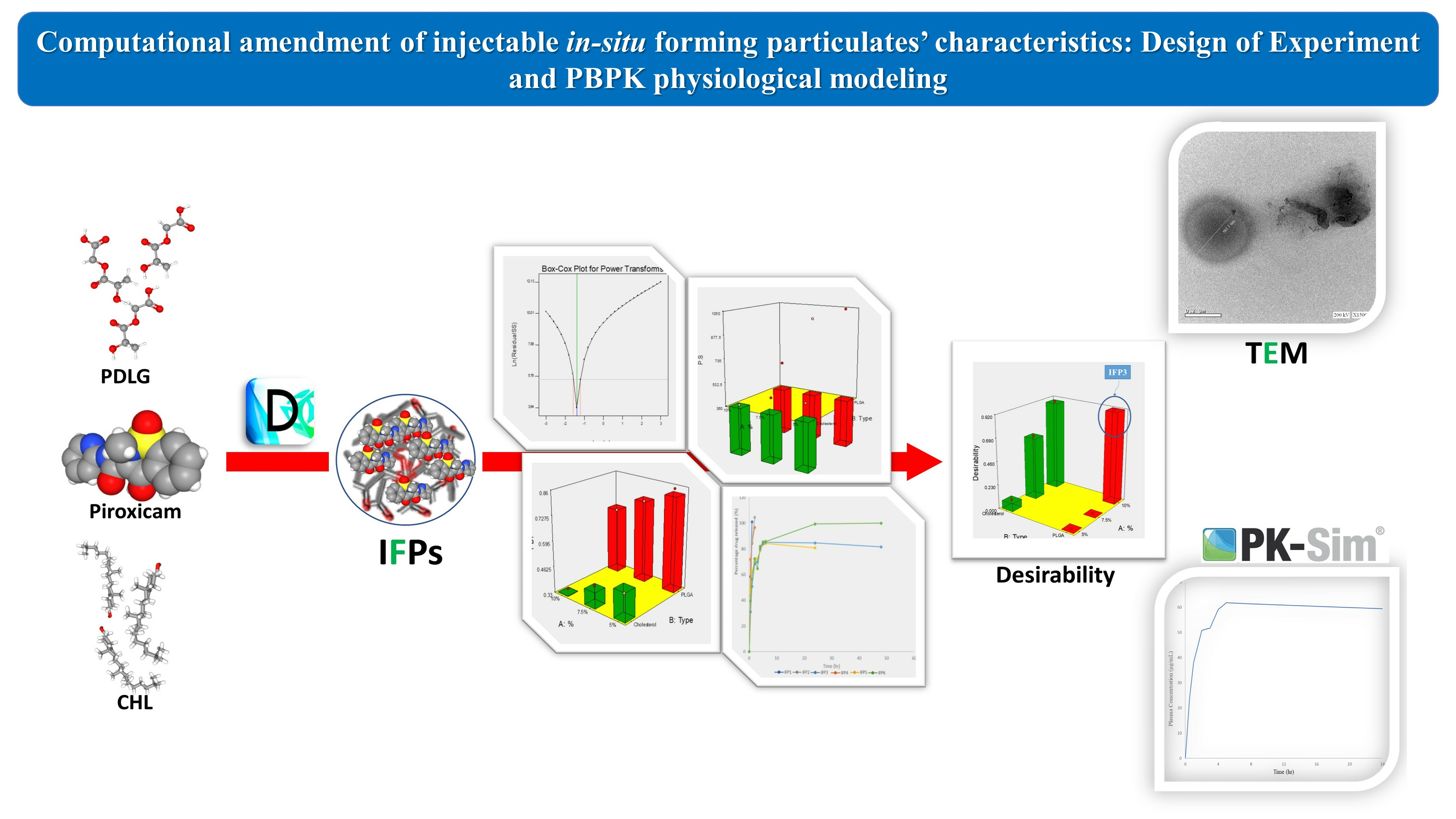
Pharmaceutics, Free Full-Text

BG - Active and passive fluxes of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus
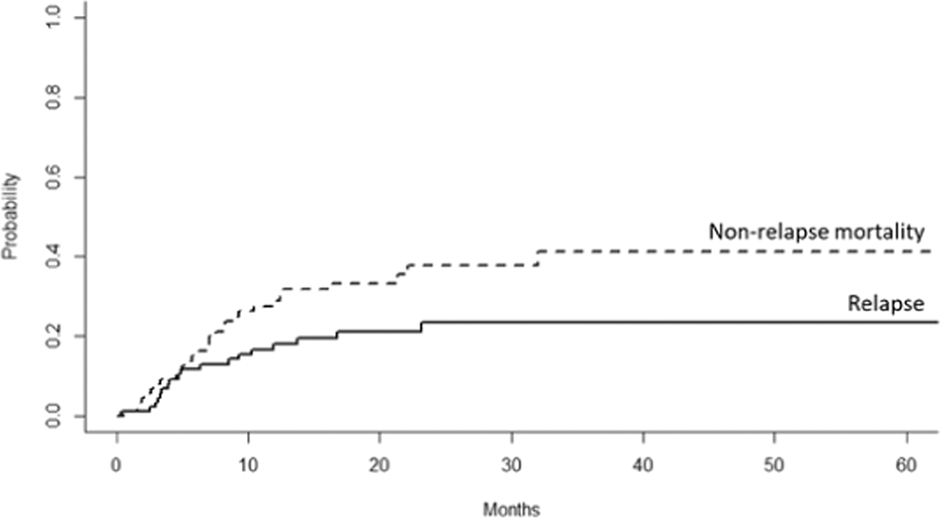
The 47th Annual Meeting of the European Society for Blood and
Read Auburn Speaks – On Food Systems by The Park at Auburn University on Issuu and browse thousands of other publications on our platform. Start here!

Auburn Speaks – On Food Systems by The Park at Auburn University